If your domain is pointed to our BasicDNS or PremiumDNS systems, you can set up A, AAAA, ALIAS, CNAME, NS, SRV, TXT, URL Redirect, MX, MXE, CAA records from Wvphost's side.
If it is not using any of them, feel free to contact your DNS/hosting provider for assistance or switch your domain to them.
A record (IPv4)
An A record (Address record) allows you to associate a domain name or subdomain with an IP address (32-bit).
This is how the record should be configured in your Wvphost account: Advanced DNS >> Host Records section: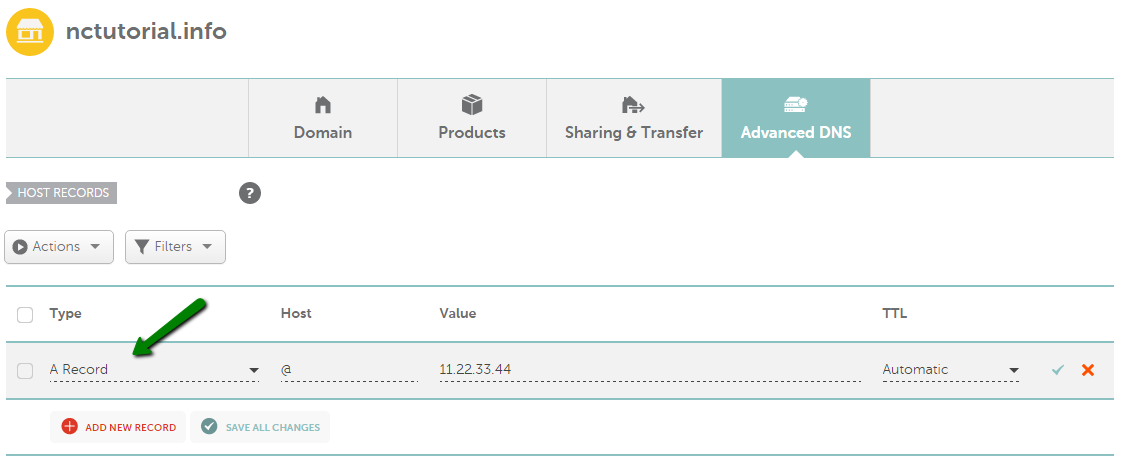
AAAA record (IPv6)
An AAAA record is similar to an A record, but it allows you to point your domain to a 128-bit Ipv6 address.
It is configured in the same way as an A record, but an AAAA Record should be selected under Type: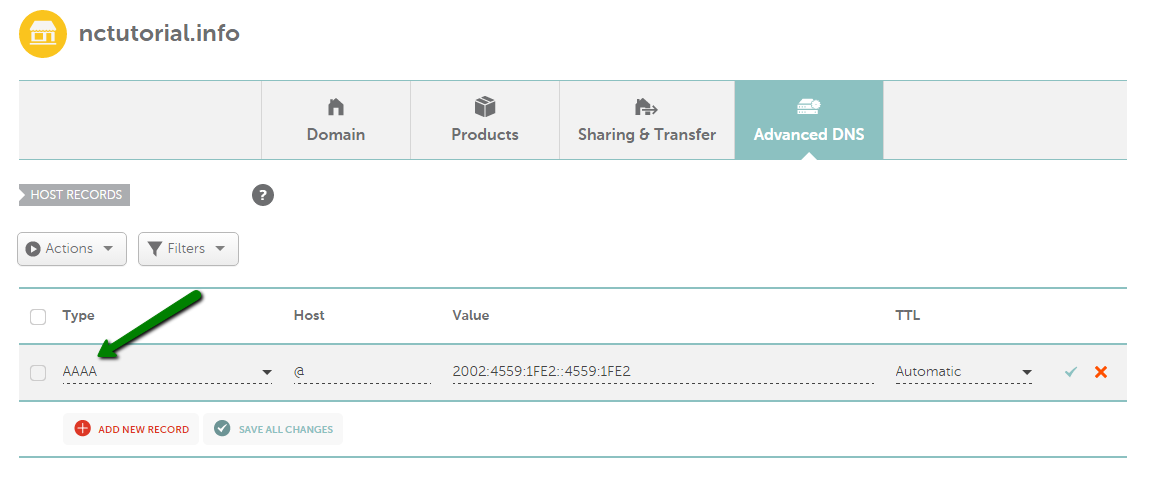
ALIAS record
The ALIAS record is a virtual host record type which is used to point one domain name to another one, almost the same as CNAME. But the important difference here is that ALIAS can coexist with other records on that name. An ALIAS record can also be used if you wish to alias the root domain to another service (which is impossible with the help of a CNAME record).
This is how the record should be configured in your Wvphost account: Advanced DNS >> Host Records section:
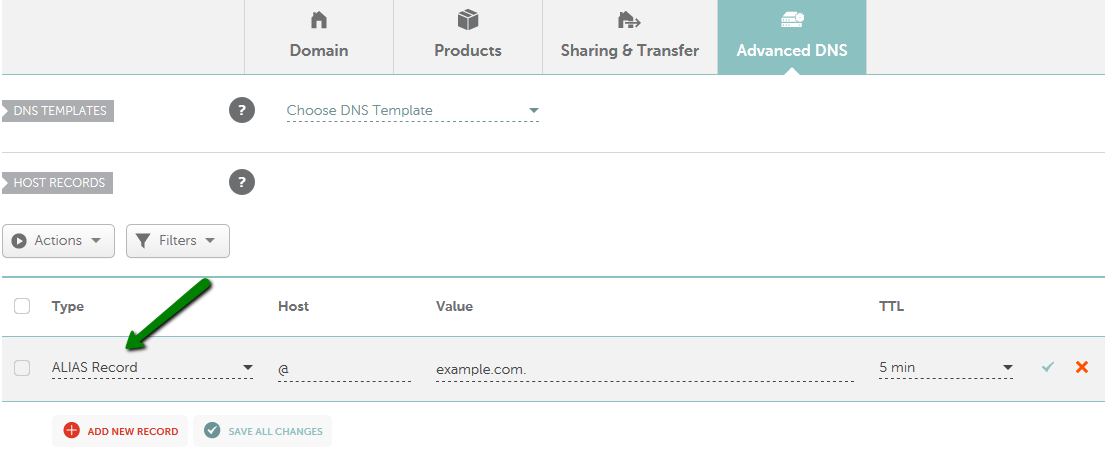
CNAME record
This record identifies a domain name as an alias of another canonical name. A CNAME record will point your domain or subdomain to the IP address of the destination hostname. This way, if the IP of the destination hostname changes, you won't need to change your DNS records, as the CNAME will have the same IP.
Please do not set up a CNAME record for a bare domain (@ hostname) since this may affect the operation of the domain's MX records and, consequently, the email service. In most cases, you will need to create a CNAME record for WWW (or other subdomain) and a URL redirect for @ that will point to http://www.yourdomain.tld/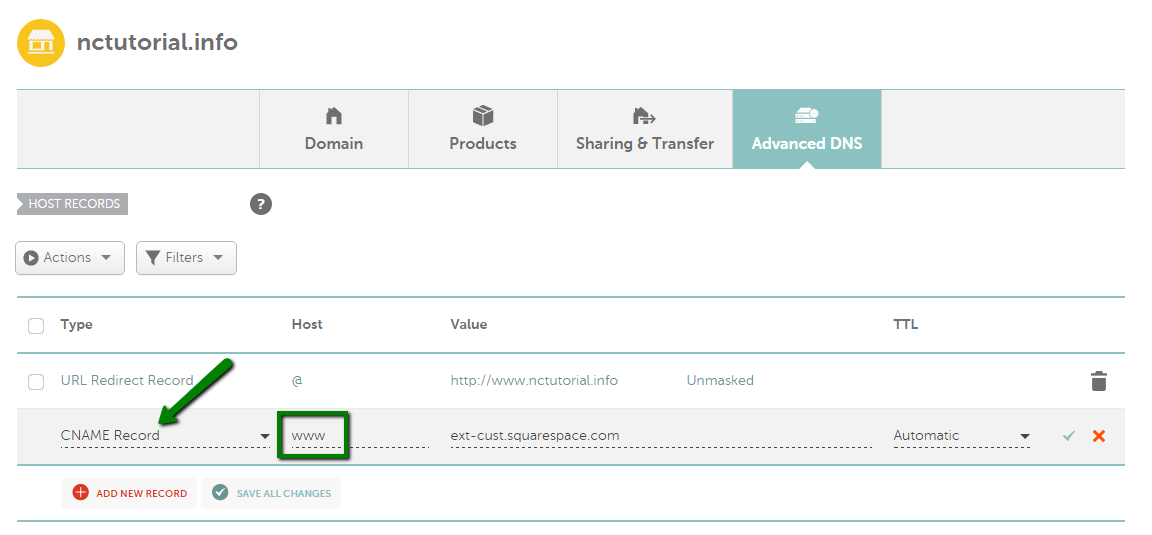
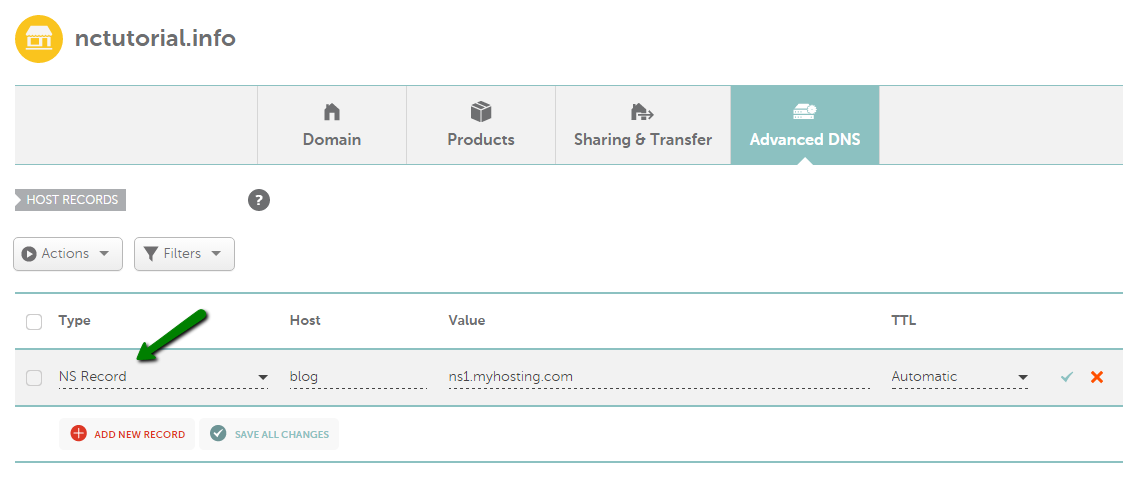
NS record
An NS record allows you to delegate a subdomain of your domain to a nameserver not associated with the domain itself. This is necessary when your subdomain is hosted separately from the domain name.
Please mind that it is *not* recommended to create NS records for a bare domain ( e.g. yourdomain.tld), as they are not used by caching DNS servers in order to determine the authoritative servers for the domain. Should you want to point yourdomain.tld to the nameservers, like ns1.server.tld / ns2.server.tld, check the following manual.
SRV record
SRV records allow you to define the location (i.e., the hostname and port number) of servers for specified services.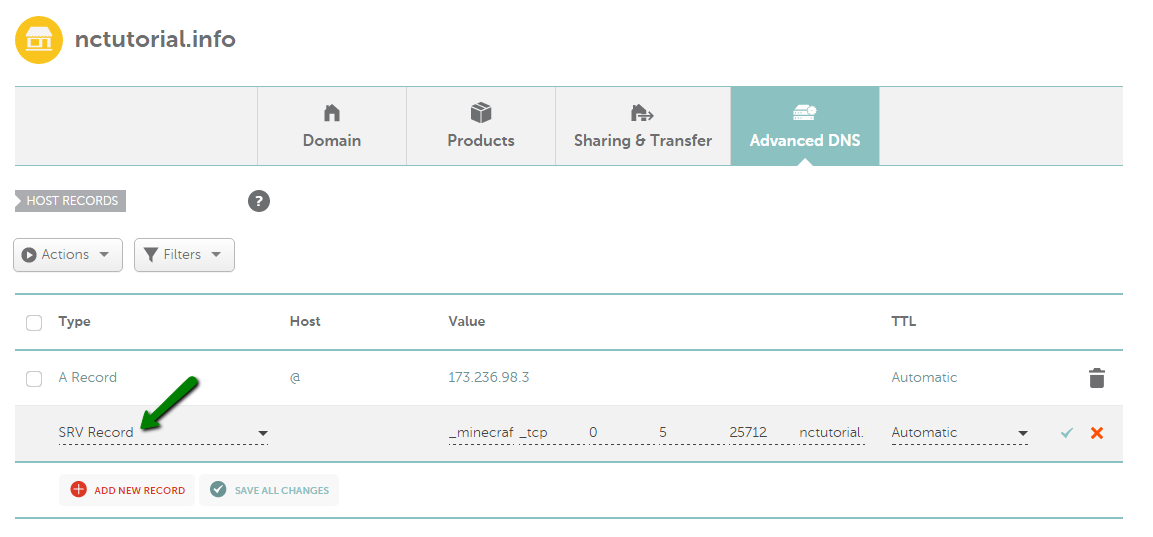
TXT record
A TXT record is used to hold text information for descriptive purposes. TXT records are often used to store SPF (Sender Policy Framework) records and to prevent people from receiving fake emails.
These records sometimes need to be set up for verification purposes. Certain Google services require it, for example.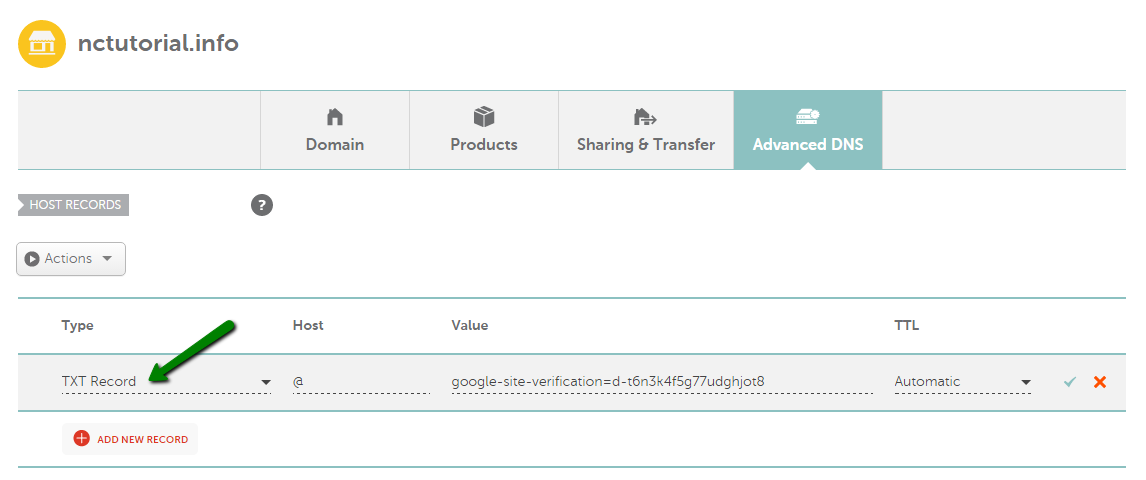
URL Redirect (Unmasked Forwarding)
This record is used to redirect a domain to another URL/domain name. When users type yourdomain.tld into the URL bar, they are redirected to any specific web page, for example, http://maps.google.com/ or http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Main_Page. In this case, the destination URL is "unmasked" or displayed in the address bar instead of yourdomain.tld.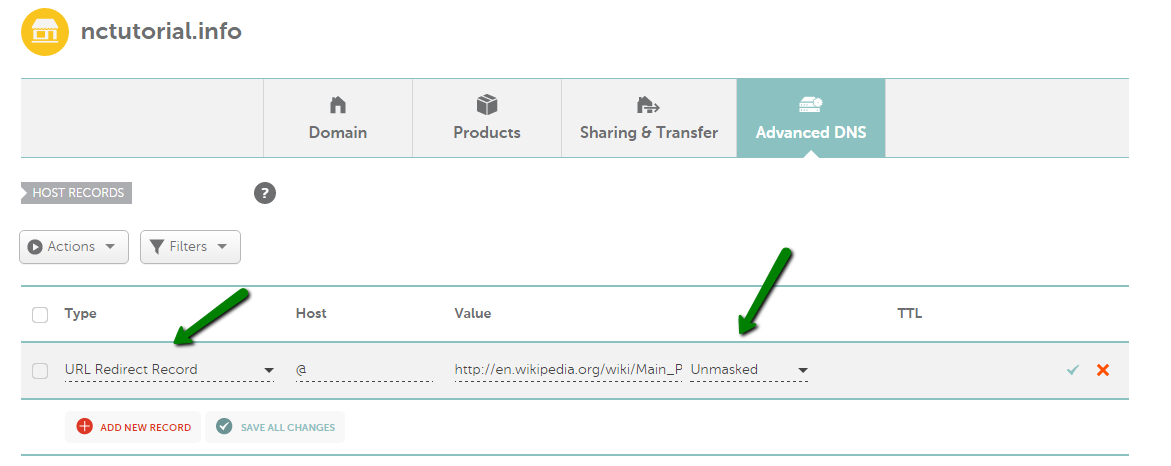
URL Frame (Masked Forwarding)
The URL Frame record is similar to URL Redirect, except that instead of redirecting the client to your web page, the web page is displayed in a frame. This way, the browser will display www.yourdomain.tld while users are on your site and not the actual URL of the page: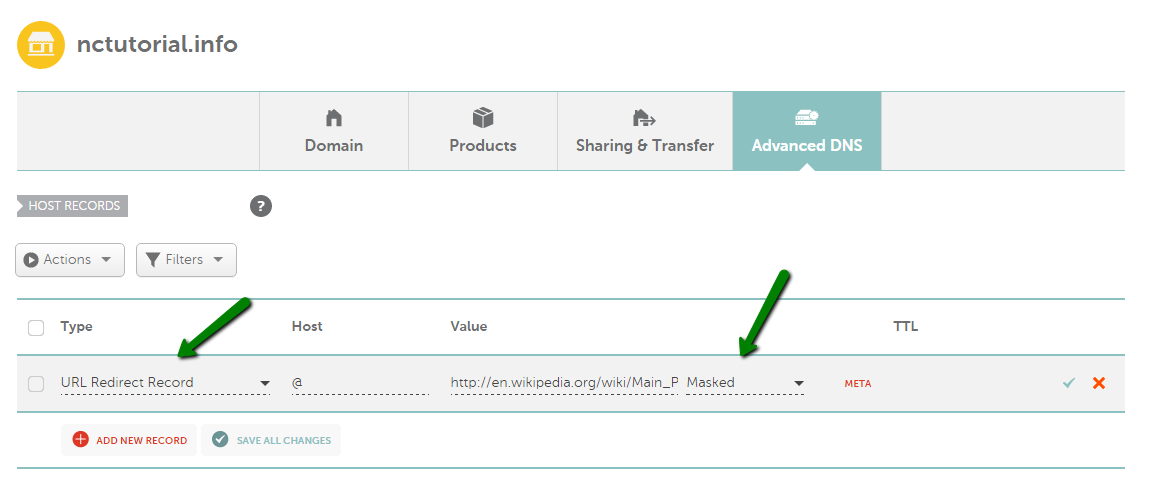
URL Redirect (301)
URL Redirect (301) This record, sometimes known as Permanent Redirect, should be used when you wish to permanently redirect your domain to a specific URL/domain name.
In this case, search engines are notified of a permanent address change and the values of internal links are transferred to the new site.
Select Permanent (301) from the Record Type drop-down menu: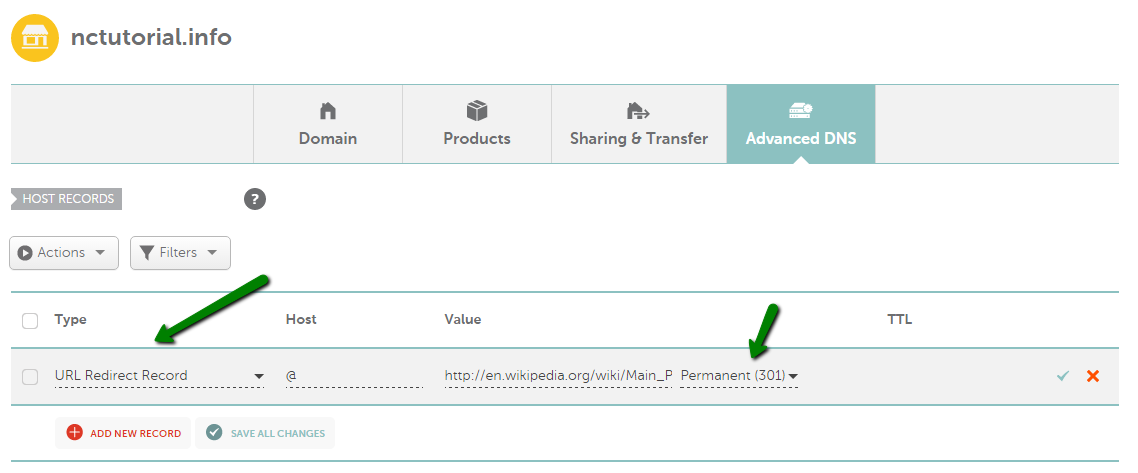
MX record
An MX (Mail) record is used to direct email to a specific mail server. Like a CNAME record, MX entries must point to a host name and should not be pointed directly to an IP address.
You will also need to set a priority for your MX record in the Priority column.
This is how the record should be configured in a Wvphost account, the Mail Settings section: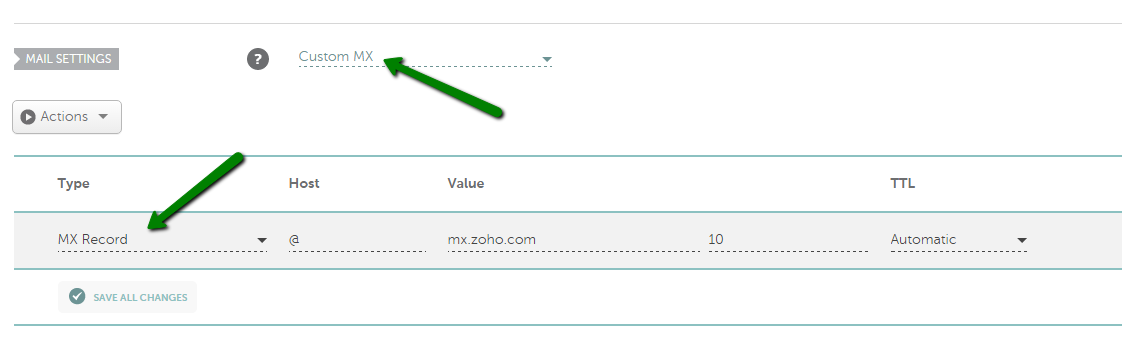
MXE record
MXE (Mail Easy) is used to forward mail to an IP address of a mail server.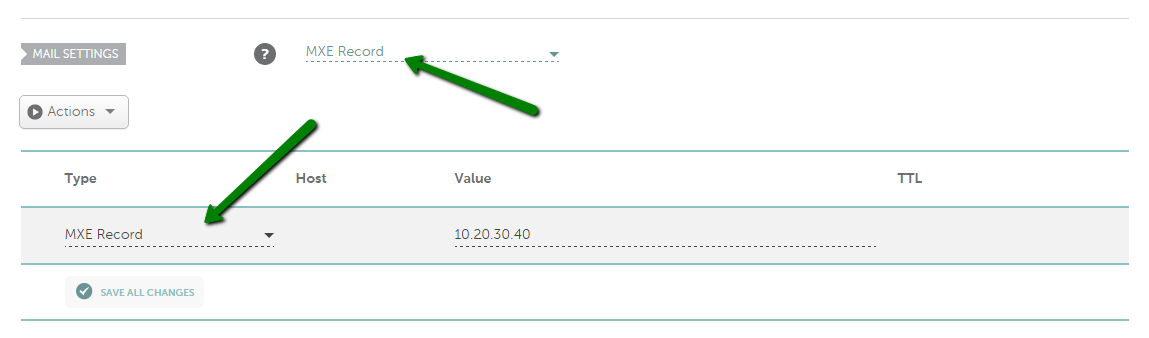
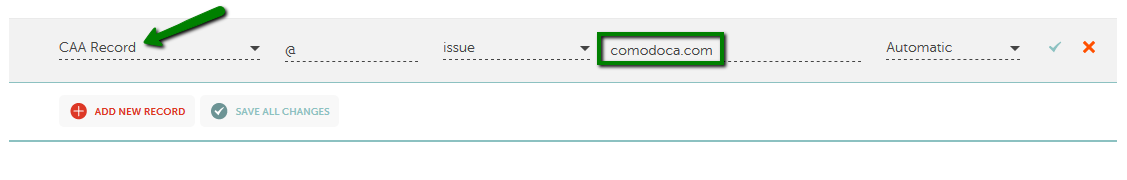
CAA record
A CAA record identifies Certificate Authorities that are allowed to issue SSL certificates for a specific domain name or subdomain.
This is how the record should be configured in your Wvphost account: Advanced DNS >> Host Records section:
NB! Usually, it may take up to 30 minutes for the <a href="https://www.wvphost.com/support/knowledgebase/article.aspx/9622/10/dns-propagation-explained/">DNS changes to propagate</a> globally.
To check more information on TTL, please refer to <a href="https://www.wvphost.com/guru-guides/what-is-time-to-live-ttl/">What is Time-To-Live and How does It Work?</a>.

